Open Prostatectomy
Overview
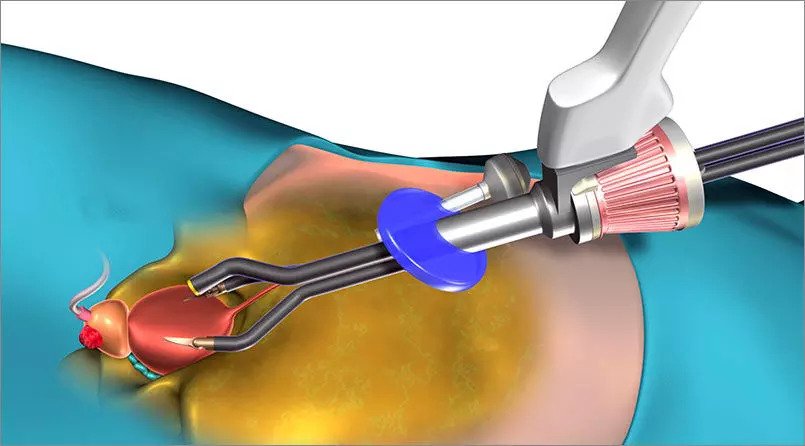
A prostatectomy is a surgical operation used to remove all or part of the prostate gland. In the male pelvis, the prostate is situated below the urine bladder. The urethra, which carries urine from the bladder to the penis, is included.
The approach is used to treat a variety of prostate-related conditions. Most frequently, it is used as a treatment for prostate disease.
Depending on the issue, there are different ways that prostatectomy can be applied. Options include open medical processes and less invasive medical treatments with automated assistance.
Why it's done
Prostate malignant growth is average, a constant reason for disease passing. The early location might be a significant apparatus for fitting and timely treatment.
Prostate malignant growth can cause raised degrees of public service announcement. Nonetheless, numerous noncancerous conditions likewise can expand the public service announcement level. The public service announcement test can identify high degrees of public service announcement in the blood yet doesn’t give exact symptomatic data about the state of the prostate.
The public service announcement test is just a single device used to evaluate for early indications of prostate disease. One more typical screening test, usually finished notwithstanding a public service announcement test, is a computerized rectal test.
In this test, your primary care physician embeds a greased-up, gloved finger into your rectum to arrive at the prostate. By feeling or pushing on the prostate, the specialist might have the option to decide whether it has strange protuberances or challenging regions.
Neither the public service announcement test nor the advanced rectal test gives your primary care physician sufficient data to analyze prostate disease. Unusual outcomes in these tests might lead your primary care physician to suggest a prostate biopsy.
Risks
- Bleeding
- Urinary tract infection
- Urinary incontinence
- Erectile dysfunction (impotence)
- Narrowing of the urethra or bladder neck
- Formation of cysts containing lymph (lymphocele)
